FREE高考英语零基础入门训练
注:本文最初发表于我的 Bilibili 专栏,属于这个视频的笔记
FREE高考英语零基础入门训练
第零章 关于英语的基本常识
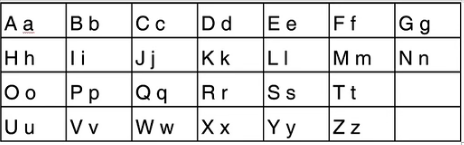
一 构成英语的基本单位—字母(书写)
二 英语的词汇
总词汇量 99万
常用词汇量 8-11万
日常生活用语 2000左右
SAT/GRE 12000以上
四级/六级 4000/6000
高考 3000-1783
三 英语的语法
1.词性
名词 (n.)表示人或事物的名称的词
动词 (v.)表示动作和状态的词
形容词(adj.)表示人或事物的特征的词
副词(adv.)修饰动词、形容词和副词的词
连词 (conj.)连接词/短语/句子与词/短语/句子
介词 (prep.)表示名词和代词与其他词的关系
代词 (pron.)是代替名词、形容词和数词的词
冠词 (art.)与名词连用,起说明人或事物的作用
数词(num.)表示数量和顺序的词
感叹词(int.)表示说话人感情或语气的词
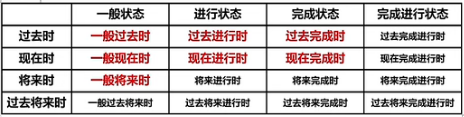
2.时态
3.与中文的差异
所有格-‘s He is Fred’s best friend
动词第三人称单数-s Fred works.
过去时-ed Fred worked.
现在分词/进行时-ing Fred is working
过去分词-en The car was stolen.
动名词-ing Working is good for us.
复数-s Fred has two blue pens.
比较级-er Fred is smarter than Rick.
最高级-est Fred has the fastest car.
第一章 简单句的基本认知
什么是句子
一组词 a group of words
有完整含义complete idea
有主语 person or thing + does or is something
有动词 what the subject does or is
例句
I understand English.
My friend reads quickly.
That cat is black.
注意
所有句子都要以大写字母开始
陈述句以句号“.”结尾
疑问句以问号“?”结尾
感叹句以叹号“!”结尾
在英语的句子中,严禁逗号连接两个句子
In the morning,l usually get up at 7 o’clock. My school is not far away.
第二章 名词的基本知识
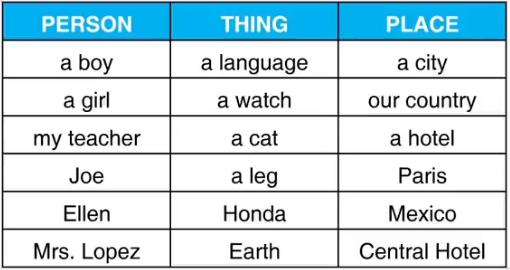
一 什么是名词
名词对人物、事物、地点命名
二 名词的单复数★
单数指一个,复数指两个或多个
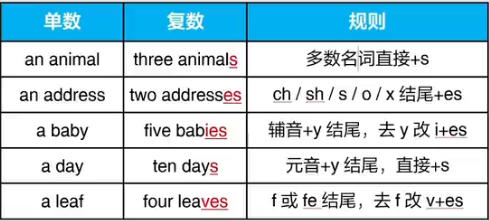
三 名词复数规则变化
1.在词尾直接加s
shop-shops desk-desks
computer-computers school-schools
face-faces house-house
2.以s、x、sh、ch结尾的词,在词尾加es-
bus-buses box-boxes
watch-watches brush-brushes
3.以结尾的词,特殊的四个词加es,其它直接加s
tomato-tomatoes potato-potatoes
hero-heroes Negro-Negroes
radio-radios photo-photos
zoo-zoos piano-pianos
4.以辅音字母+y结尾的词,y变成i加es
baby-babies city-cities
factory-factories story-stories
元音字母5个a e i o u
辅音字母21个
5.以f或fe结尾的词
f变成v加es
thief-thieves shelf-shelves
wolf-wolves leaf-leaves
self-selves half-halves
wife-wives knife-knives
life-lives
直接加s
roof-roofs belief-beliefs
proof-proofs gulf-gulfs
handkerchief-handkerchiefs
6.名词复数不规则变化
(1)常见特殊变化
man-men woman-women
child-children foot-feet
tooth-teeth goose-geese
mouse-mice
(2)单复数同形
Chinese/Japanese/deer/sheep/fish
(3)只有复数没有单数
people/shoes/glasses/gloves/shorts/clothes/socks/trousers/pants/scissors
四 可数名词与不可数名词
可数名词可以变复数形式
不可数名词没有复数形式,只有单数形式
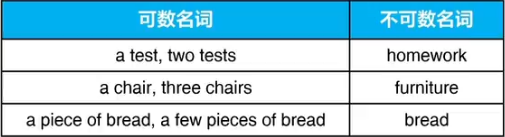
注意
1 不可数名词只用单数,不和a/an及数词搭配使用。
2 不可数名词表示数量时,需要使用量词。
a piece of news 一条新闻
two pieces of bread两块面包
three pieces of paper三张纸
four glasses of milk四杯牛奶
five bottles of water五瓶水
six cups of tea六杯茶
1.食物相关的不可数名词
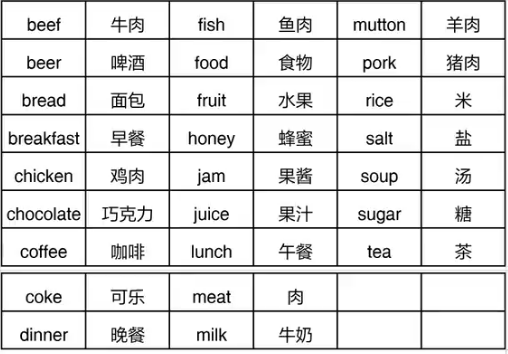
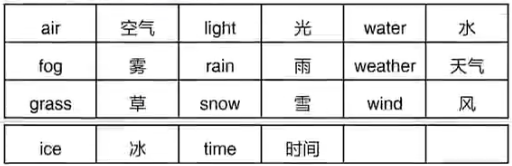
2.自然相关的不可数名词
3.具体事物相关的不可数名词
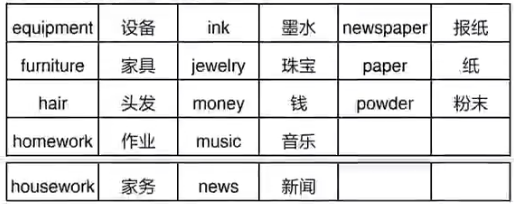
4.抽象概念相关的不可数名词
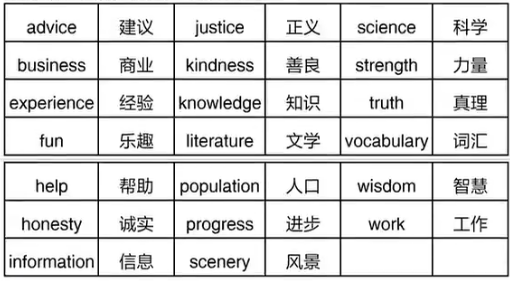
五 专有名词的书写规则
专有名词指特定的人物、事物或地点的名字
单个词汇的专有名词首字母大写
多个词汇的专有名词每个单词的首字母大写
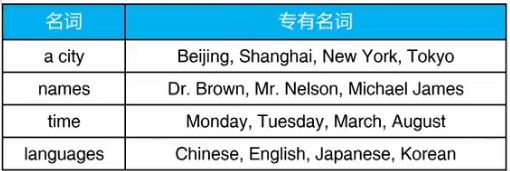
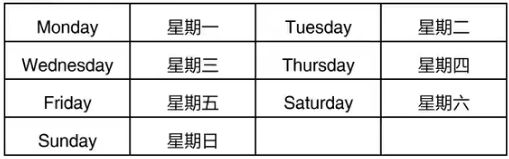
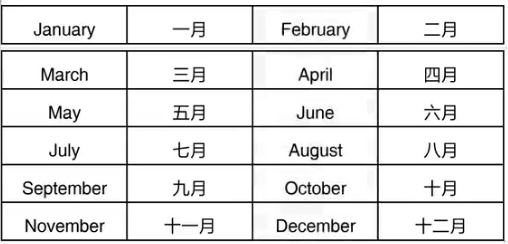
1.月份与星期的名称
2.人名的书写方法
外国人名 Michael 名 James姓
中国人名 Tao 姓 Ran名 /Ran名Tao姓
Tao姓Ranran名
七 动名词与动作的名词形式
read动词 -reading名词
write动词 -writing名词
learn动词 -learning名词
collect动词 -collection名词
注意:如果某个动词有专属的名词形式,则避免使用动名词
shopping swimming climbing
八 冠词:对名词进行限制
不定冠词 a/an 定冠词 the 零冠词 /
注意:单数名词禁止裸奔,必须加限制词
限制词的种类
1 冠词a table/the table
2 指向形容词this table/that table/these tables
3 归属形容词my table/your table/his table
4 数量词 one table/two tables
5 冠词+形容词a red table/a wooden table
注意:复数名词和不可数名词可以使用the,不使用a/an,不一定需要限制词(the) money/some money/a lot of money
much money /little money
不定冠词a/an不确定某一个 general 概括
I want to see a movie this weekend.
元音前使用an辅音前使用a
特别:a university /ju:/ a unique person
an umbrella an uncle
an hour an honest boy
a half
定冠词 the 确定 这个/那个 specific 具体
I want to see the movie this weekend.
第三章 动词的一般现在时
一 英语句子的基本要求
一组词,有完整含义,有主语,有动词
大写字母开头,句号问号叹号结尾
二 动词最基本的时态:一般现在时(广义现在)
狭义现在:当前这一瞬间
广义现在:不分过去现在将来
发生许多次的动作 actions that happen many times
一直都这样的动作 actions that are always true
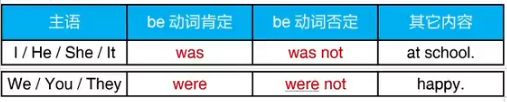
三 英语中最基本的动词:Be动词 “是” “=”
1.Be动词一般现在时的三种形态
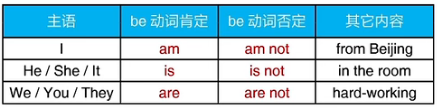
2.Be动词的缩写形式
I am-I‘m
he is-he‘s
she is-she‘s
it is-it‘s
we are-we‘re
you are-you‘re
they are-they‘re
I am not-I am not
he/she/it is not-he/she/it isn’t
we/you/they are not-we/you/they aren’t
注意:
1.you可以表示“你”或“你们”
2.缩写格式在正式写作中禁止使用
3.Be动词和主语的单复数保持一致(非常重要) *动名词视作单数
3.Be动词的常见句型
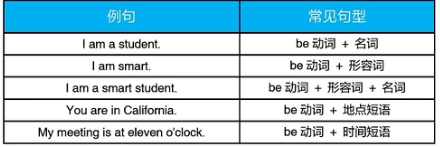
注意:常见错误
缺动词 Mary is a good person.
与主语不一致 The boys is are in the kitchen.
否定形式不正确 That computer no is not expensive.
4.Be动词的重要句型:There be句型
there is/there are+主语+介词短语补充
用于表示某物存在,或某处有某物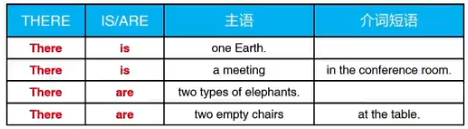
四 表达时间和地点:介词短语
一组词,以介词开始,包括一个名词或代词
这个名词或代词叫做介词的宾语
1.表示地点的介词短语(place/location)
回答where的问题,一般放在句子末尾
We eat a lot of salad at home.
The computer is on the desk.
Loretta lives in my house.
2.表示时间的介词短语(time)
回答when的问题,一般放在句尾
如果与地点短语同时出现,时间一般放在地点后面
Michelle reads the news paper in the morning.
She sees him at the bank on Mondays.
3.不需要介词的时间词和时间短语
Eric watches TV daily.
Marco works every afternoon.
注意:
如果地点短语或时间短语放在句首,则要用逗号断开
ln the spring, everyone has finals.
To day, we have an important meeting.
Twice a week, Teresa volunteers at the library.
4.常见的地点和时间短语
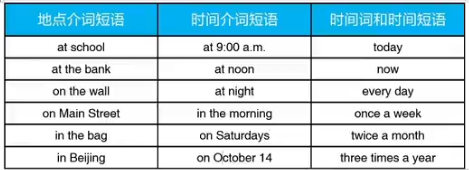
五 常规动词的一般现在时
1.常规动词的一般现在时形态
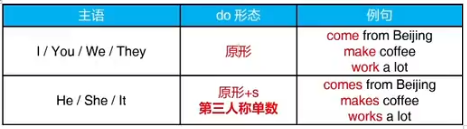
2.第三人称单数动词的特殊变化
(1)s/x/sh/ch/z结尾的动词,加es
wash - washes
pass -passes
watch-watches
mix -mixes
fix-fixes
(2)辅音+y结尾的动词,去y改i加es
cry - cries
try-tries
bury - buries
marry - marries
play -plays
say -says
buy - buys
(3)不规则变化的动词
have-has
do-does
go-goes
注意:常见错误
缺动词 Ed and Linda live in Texas.
第三人称单数错误 Ed works in a big office.
多个动词混用 Ed is wakes up at 6 a.m. every day.
第三人称单数错误 Ed tries to sleep seven hours every night.
如果用到be动词或常规动词的一般现在时,不允许同时出现两个一般现在时的动词连用
3.常规动词一般现在时的否定表述
一般现在时变否定,前面加入助动词do not/does not
原来的动词使用原形do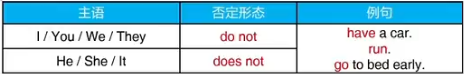
注意:do not可以缩写为don’t,does not可以缩写为doesn’t,不建议在写作里使用
第四章 动词的一般过去/将来时
一 关于英语的时态
时/时间:过去、现在、将来、过去将来
态/状态:一般、进行、完成、完成进行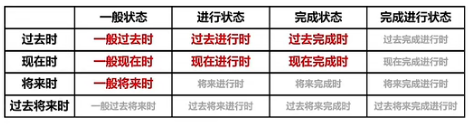
二 关于英语里的时间概念
广义现在:任何时间
狭义现在:当前这一刻,当前的一瞬间
过去:现在之前,与现在完全没有关系的时间
将来:现在之后,还没有到来的时间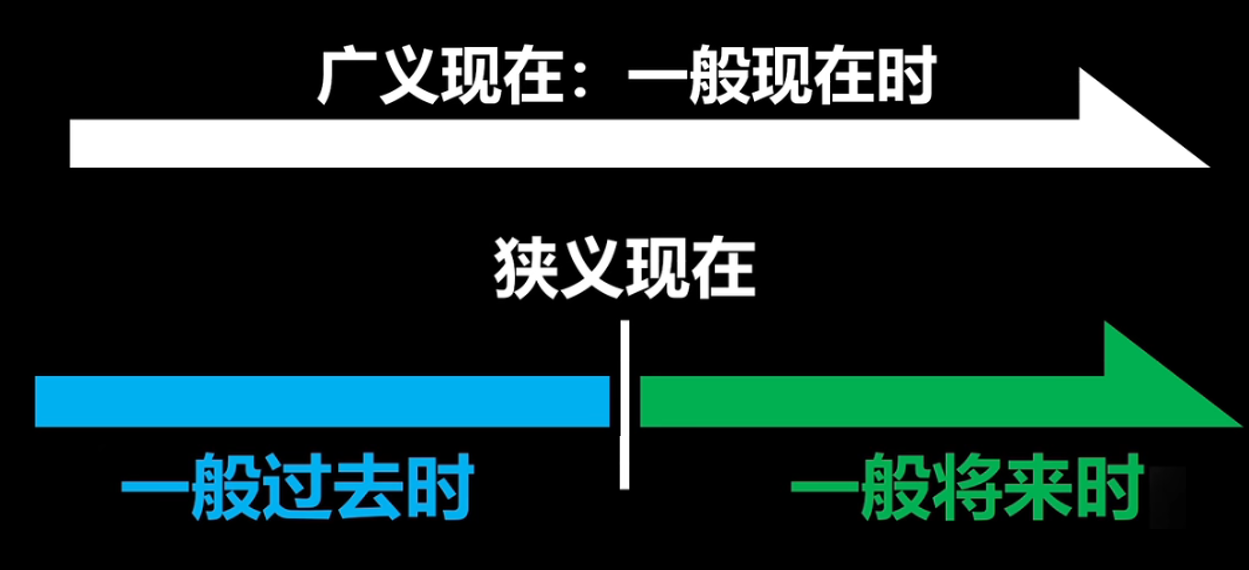
三 一般过去时
1.概念:
在过去发生的动作 actions that happen in the past(句子的动词体现动作时间)
2.动词的变化
(1)规则变化 -ed
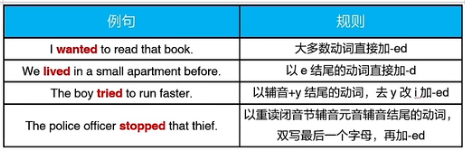
需要双写加-ed的常见动词,共30个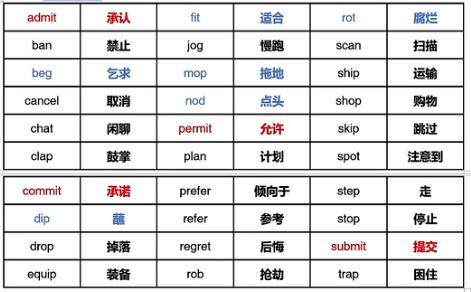
(2)不规则变化,共100词
1)Be动词
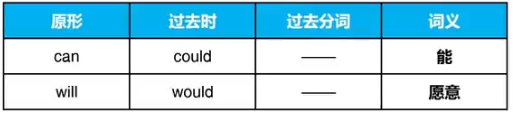
2)情态动词,共2词
3)常规动词
①三种形态相同AAA,共9词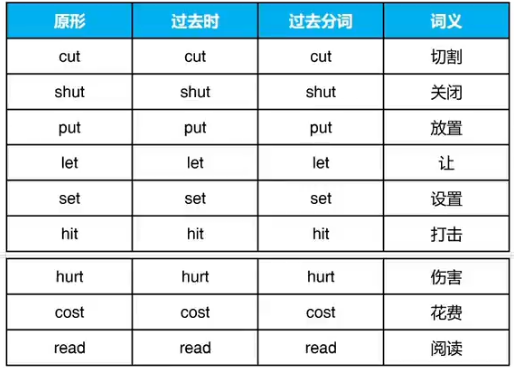
②原形与过去时相同AAB,共1词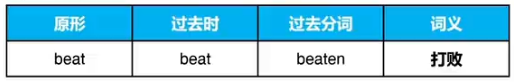
③原形与过去分词相同ABA,共3词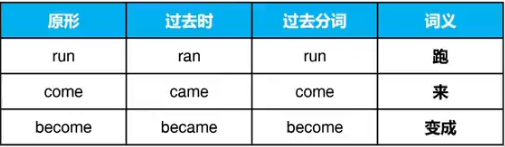
④过去时与过去分词相同ABB,共43词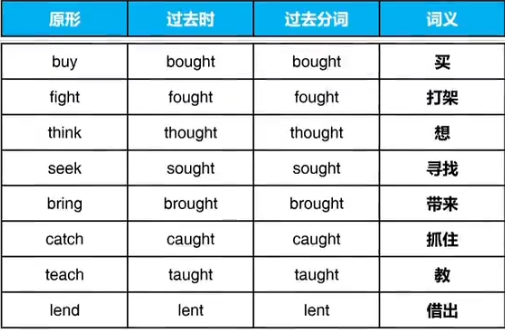
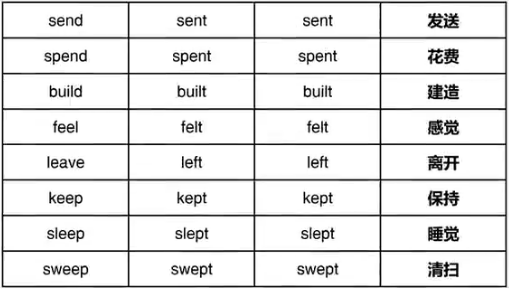
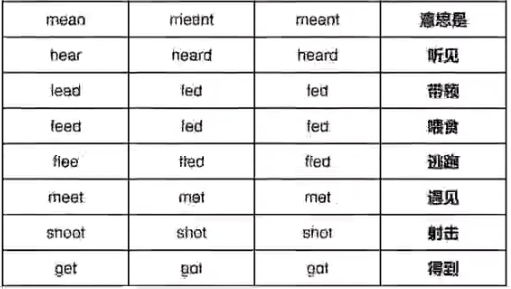
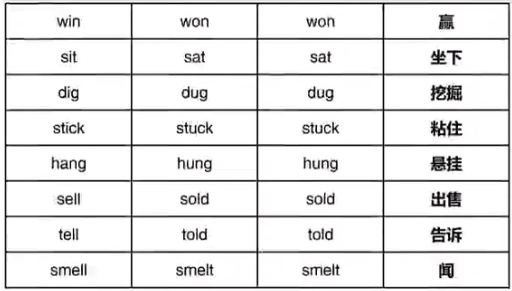
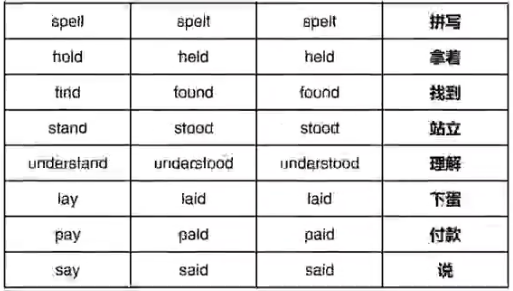
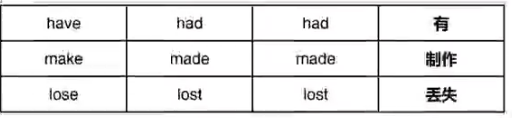
⑤三种形态均不相同ABC,共41词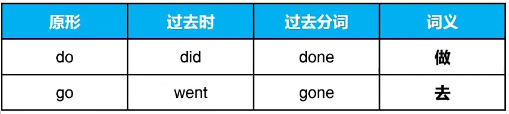
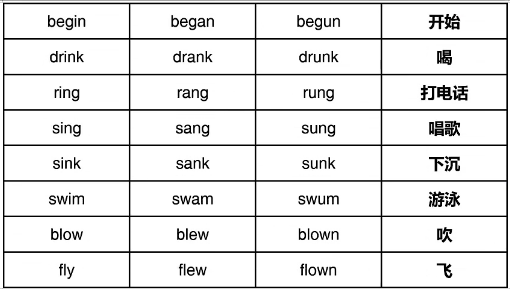
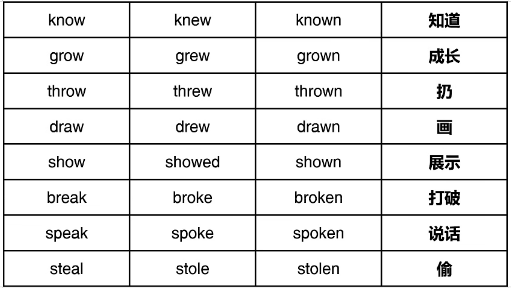
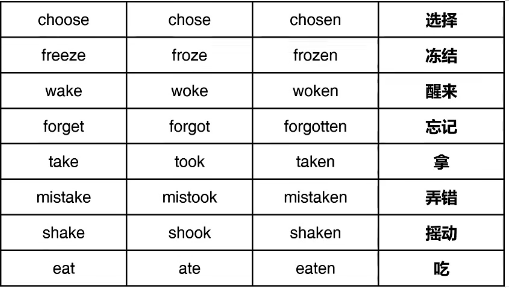
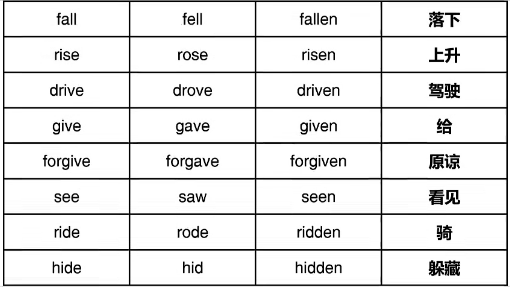
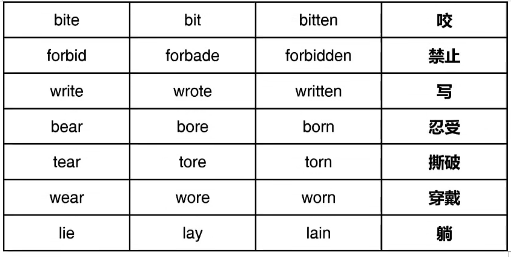
注意:常见错误
时态错误 We lived in London in 2010.
动词不规则变化错误 She went to Brazil in 2005.
动词冲突 I was took Bus 300 yesterday.
3.常见的过去时间
yesterday
We played soccer yesterday.
last+时间词
last night last week last month..
I finished my homework early las night
数字+时间词+ago
two hours ago,three days ago,four weeks ago…
She arrived here two weeks ago.
注意:如果时间短语放在句首,需要逗号断开
写句子必须注意的三个要素:
句首大写字母、句尾标点符号、动词时态变化
Yesterday, we played soccer.
Last night, I finished my homework early.
Two weeks ago,she arrived here.
4.否定表述
一般过去时变否定,加入助动词 did not
原来的动词使用原形 do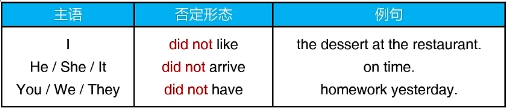
注意:did not可以缩写为didn’t,不建议在写作里使用
注意:常见错误
未使用助动词 Andrea did not live in Korea in 2011.
助动词时态错误 We did not arrive late.
动词未改原形 I did not take the bus yesterday.
动词冲突 Norah did not wake up at 7 this morning.
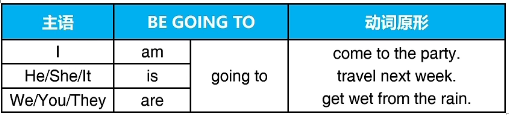
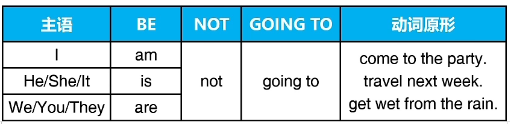
四 一般将来时will/be going to
1.适用范围:
预测和预期 predictions & expected results
计划和提议 plans & proposals
2.使用be going to表示将来
(1)适用范围
已经制定好的计划 future plans that already made
基于现在行为的预测 predictions based on a present action
(2)使用方式
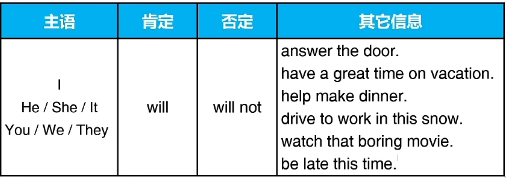
3.使用will表示将来
(1)适用范围
现在作出的未来的计划或决定 future plans/decisions
语气较强的预测 strong prediction
承诺或提供帮助 promises or offering help
(2)使用方式
(3)will 的缩写形式
I will - I’ll
he will - he’ll
we will - we’ll
she will - she’ll
you will - you’ll
it will - it’ll
they will - they’ll
will not - won’t
注意:在写作中尽量避免使用缩写形式
4.常见的将来时间
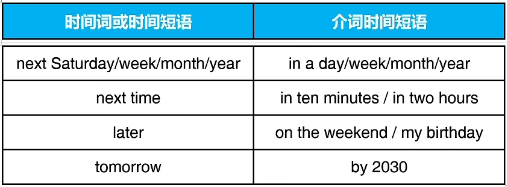
注意:如果时间短语放在句首,需要逗号断开
We are going to go to the movies on Saturday.
=On Saturday, we are going to go to the movies.
The airline will use a new kind of jet next year.
= Next year, the airline will use anew kind of jet.
第五章 代词的基本知识
一、什么是代词(代词概念)
代词是替代名词、短语或句子的词
替代名词 I live in China. She is a great country.
替代短语 There are a lot of beautiful flowers in the garden. Some are white and some are red.
替代句子 We should respect the elders. I know that from my childhood.
二、人称代词、反身代词、物主代词
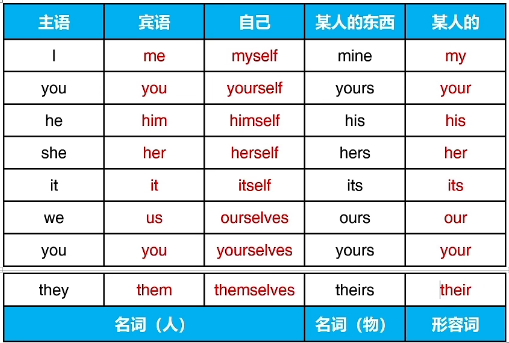
注意:宾语可以在动词后面,也可以在介词后面
注意:
1、l 在任何情况下都要大写
2、She 可以描述国家、城市或宠物,表达特殊情感
3、We 可以体现作者与读者之间的亲密关系
4、It 可以指代天气、环境、时间,还可用于形式主语、形式宾语和强调句型
自己:对自己做动作,或强调本人
l am teaching myself computer.
(You) Take good care of yourself.
The child himself drew this picture.
You should ask the children themselves.
注意:“自己”永远用在宾语,如果用在主语需要同位语
某人的、某人的东西
I love my country. 形容词
Is this your car? 形容词
That car is mine (my car), not yours (your car). 名词
These books are ours (our books). 名词
Whose bag is it? It’s hers (her bag). 名词
Yesterday I met a friend of mine (my friends) in the street. 名词
注意:常见错误
代词性别错误 Maria is my friend. She is nice.
代词单复数错误 Where are my keys? I cant find them.
代词主语冲突 My mother she is 42 years old.
自己不能作主语 I myself drive the car.
对自己作动作用自己 You should be proud of yourself.
某人的东西 May I use your pen? Yours works better.
某人的 We should learn our own culture.
三、指示代词
表示时间或空间上的远近关系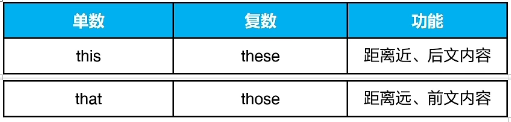
this 和 these 表示距离近
that 和 those 表示距离远
e.g. This is a book.
These are cars.
l am busy these days.
I was busy those days
That is not a room.
Those are trees.
this 和these 指代后文内容
that 和those 指代前文内容
e.g. Please remember this: no pain no gain.
I got up late. that is why l missed the bus.
重要考点:one,that 和it的区别
I can’t find my hat. I think l must buy one. 范围的某一个
This hat is bigger than that of mine. 同类的另一个
I can’t find my hat. I don’t know where l put it. 完全相同
四、疑问代词、连接代词
针对名词内容进行提问的,叫做疑问代词
替代名词内容并连接两个分句的,叫做连接代词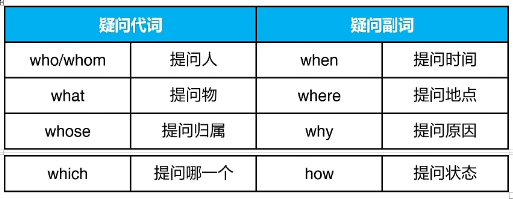
whom 宾格可以用 who 代替,介词后只用 whom
e.g. Who is here just now?
Who/Whom are you looking for?
To whom did you speak on the campus?
whose 表示“谁的”
e.g. Whose are these books on the desk?
Whose books are these on the desk?
what没有指定范围,which需要指定范围
e.g. What book do you like?
Which book do you like, this one or that one?
疑问代词可以连接两个分句,其它代词不可以
e.g. What we should do is still unknown.
I know who is waiting for you.
I met many people in my trip, each of whom was nice to me.
疑问词+ever 表示“无论”,用于加强语气
e.g. He does whatever she asks him to do.
I’ll give the ticket to whoever wants it.
Whichever team gains the most points wins.
whenever 无论何时 / wherever 无论何地 /However 无论如何
五、不定代词
不明确指代特定名词的,叫做不定代词
e.g. Everybody should be here in time tomorrow.
I know nothing about it.
That’s all l know.
1.基本不定代词

2.其它不定代词
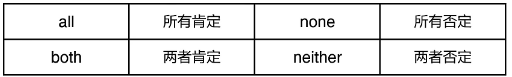
e.g. All goes well.
All the students are here.
None of the milk is expensive. 不可数用单数
None of the films is/are worth seeing. 可数随意
Both of us can speak English. 两个人
Neither of us can sing. 两个人
Both Jessy and David are good at English.
Neither you nor he can finish the work in an hour.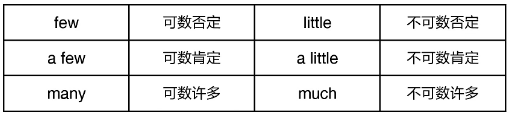
e.g. Few of the books are cheap now.否定
A few friends came to see me yesterday. 肯定
There is little water in the bottle. 否定
I have a little money to buy the book. 肯定
I have many books to give you.
We have much to say about verbs.
Many of the students like English very much.
Much of the work is easy.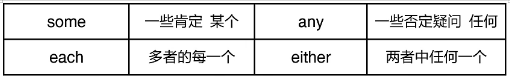
e.g. I have some books. 一些
Do you have any books? 一些
There isn’t any ink in my pen. 一些
I am going to get some ink. 一些
You can come any time. 任何
Will you have some coffee? 某个
She gave each child two apples.
Each of us must take responsibility for our own actions.
Either of them will agree to this arrangement.
Either of the two boys is clever.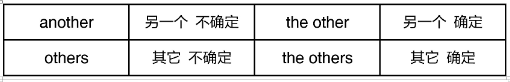
e.g. This glass is broken. I want another.
There are two glasses. One is full. The other is empty.
Some believe it is true. Others doubt it.
There are 40 students in my class. 28 are boys. The others are girls.
3.相互代词
each other /one another 互相
e.g. People should love one another.
People of different cultures always copy each other.
第六章 形容词的基本知识
一、什么是形容词
形容词是给出人物、事物或地点相关信息的词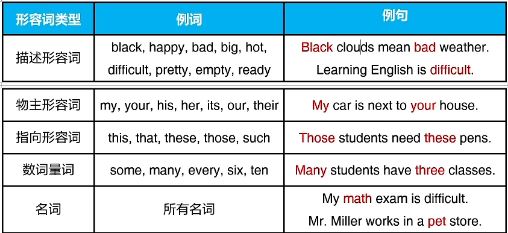
二、描述形容词
1.描述形容词的基本用法
描述形容词:用于描述名词
可以放在名词前面,或放在be动词后面
e.g. We have a new clock.
The clock is new.
描述形容词不受名词单复数变化影响
e.g. We have a new clock.
We have two new clocks.
注意:常见错误
形容词位置错误 I have a car red. - I have a red car.
形容词没有单复数 She has ten reds apples. - She has ten reds apples.
2.最基本的描述形容词
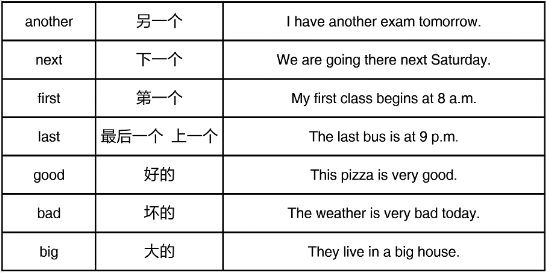
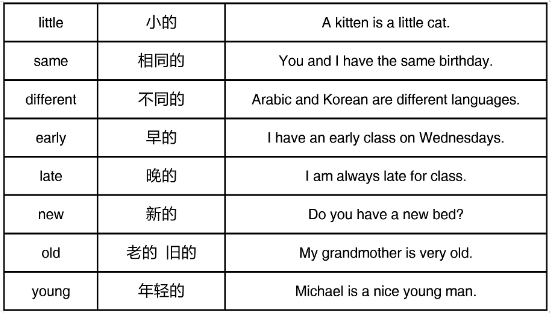
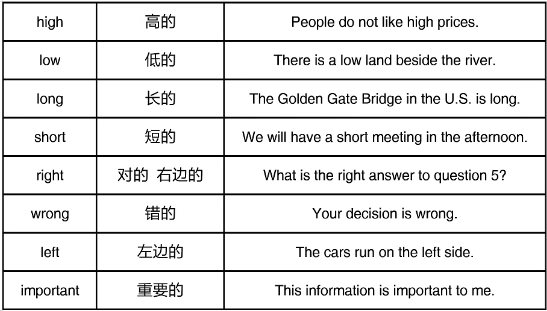

3.描述形容词的常见结尾

4.描述形容词变成副词:重要考点
基本变化:在形容词末尾加 -ly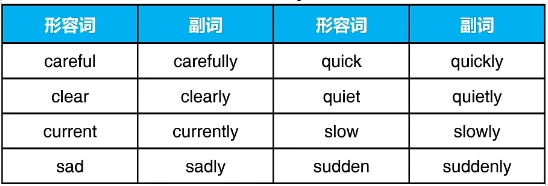
以y结尾且读音为/i/的形容词,去 y 改 i 再加 -ly
以y结尾且读音为/ai/的形容词,直接加 -ly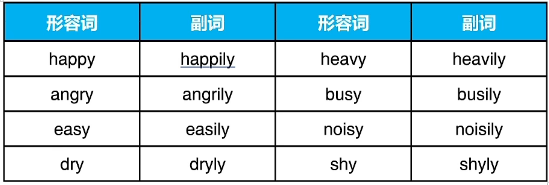
以ic结尾的词,加-ally(public 例外)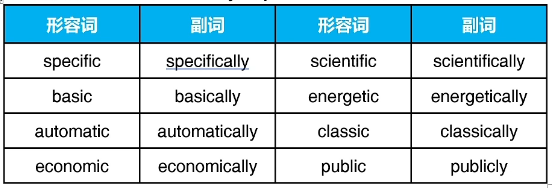
大多数辅音字母加 e 结尾的形容词,直接加-1y
少数以 e 结尾的形容词,去掉 e 再加-ly
大多数元音字母加 le 结尾的形容词,直接加-1y
辅音字母加 le 结尾的形容词,去掉 e 加-y
以 ll 结尾的形容词,直接加 y
简化记忆:12个词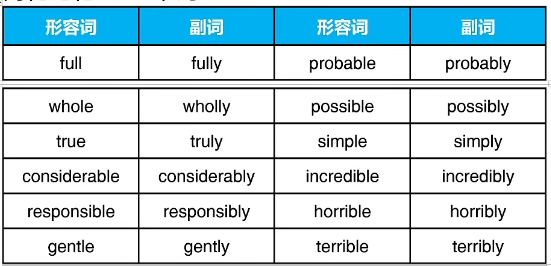
全部真正相当负责的温柔可能简单的不可思议的可怕
★个别形容词和副词词形完全一致
5.描述形容词的排序
观点 pretty,terrible,lovely,nice
形状 long,short,round,narrow
年代 old,new,young
颜色 green,blue,orange
国籍 American, Canadian, German
材质 plastic,metal,wooden
简化口诀:美小圆旧黄,法国木书房(主观一客观)
三、物主形容词
物主形容词:体现某人拥有某物
注意:常见错误
性别错误 Mary has her doctor appointment today.
形式错误 They have their laptops.
形式错误 I do not have my book.
四、指向形容词
指向形容词:用于指出特定的名词
指向形容词有单复数变化
注意:常见错误
单复数错误 This lesson is simple
语序错误 These books are very good.
五、名词作形容词
使用名词作形容词时,第一个名词描述第二个名词
名词作形容词时必须为单数
my Tuesday class = my class on Tuesday
a math test =a test about math
a shoe store = a store that sells shoes
第七章 And的常规用法
一、什么是连词
连词是发挥连接作用的词
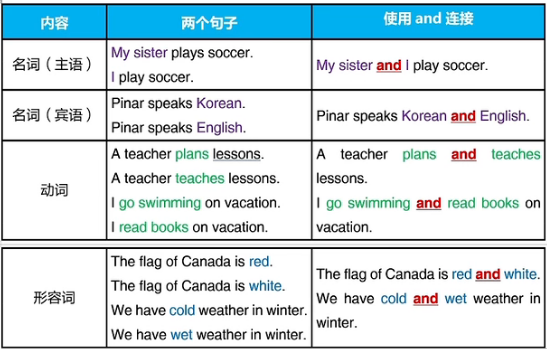
二、And的基本用法
And用于连接一个词/短语和另一个词/短语,另一个词/短语必须具备相似的信息
三、And的进阶用法:列举
使用and可以连接三个或以上的内容,最后一个内容前用and连接,其余内容后面需要有逗号断开。(如果并列的是短语,建议and之前的逗号不要省略)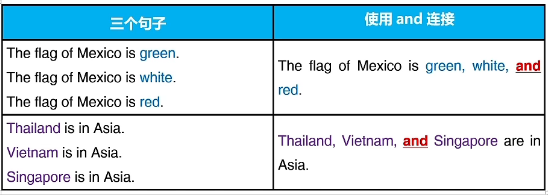
注意:常见错误
两者and不需要逗号 Miami, and Orlando are in Florida. - Miami and Orlando are in Florida.
三者以上列举需要逗号 The salad has lettuce tomatoes olives and green onions. - The salad has lettuce, tomatoes, olives, and green onions.
动词和主语保持一致 A boy and a girl is waiting for you. - A boy and a girl are waiting for you.
使用and注意名词单复数变化 English and Chinese are useful subject. - English and Chinese are useful subjects.
四、And连接句子:延伸句子内容(高考考点)
第八章 介词的基本知识
一、介词是什么
介词用于体现名词和句子里其它词的关系
二、单个词的介词

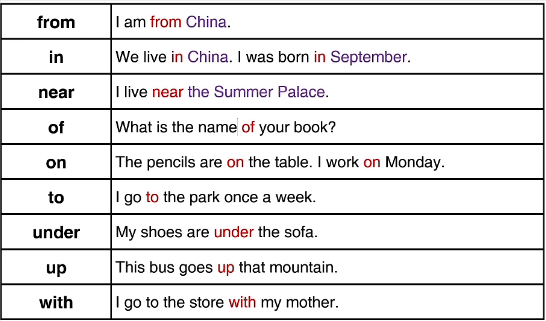

三、多个词的介词

四、介词短语:介词+名词/代词
一组词,以介词开始
包括一个名词或代词,也就是介词的宾语
介词短语主要内容:什么时间、什么地点、什么方式
l eat lunch after my class.什么时间
The Summer Palace is in Beijing.什么地点
He likes to work by himself.什么方式
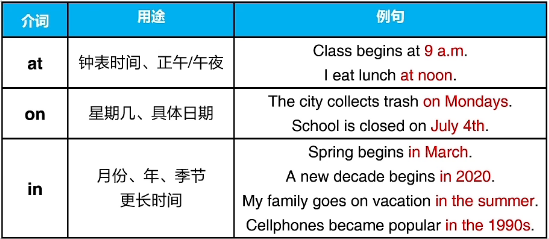
五、时间短语
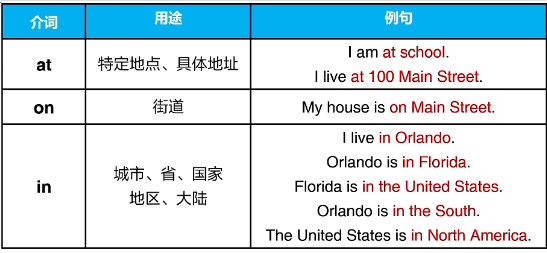
六、地点短语
注意:
1、同时使用时间短语和地点短语:先地点,后时间
place 地点 time 时间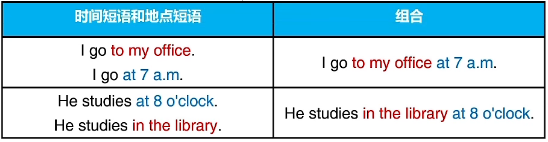
2、介词短语放在句首时,需要逗号断开
In Japan, people drive on the left side of the road.= People drive on the left side of the road in Japan.
In April, Japanese students start school.= Japanese students start school in April.
3、介词短语放在句中时,用于描述前面的名词,不影响动词变化
注意:常见错误
介词错误 Miami and Orlando are on Florida.- Miami and Orlando are in Florida.
介词缺失 I like to listen to music my car.-I like to listen to music at/in my car.(in 在车里/at 在车那)
地点时间顺序错误 Ed goes on Tuesdays and Thursdays to his classes.-Ed goes to his classes on Tuesdays and Thursdays.
缺少逗号 On the weekends I go to the beach.- On the weekends, l go to the beach.
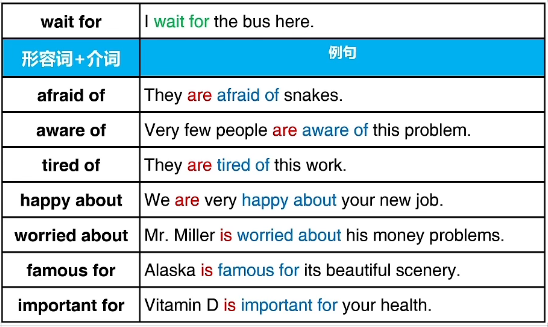
七、介词与动词或形容词组合
某些动词或形容词需要后面出现介词配合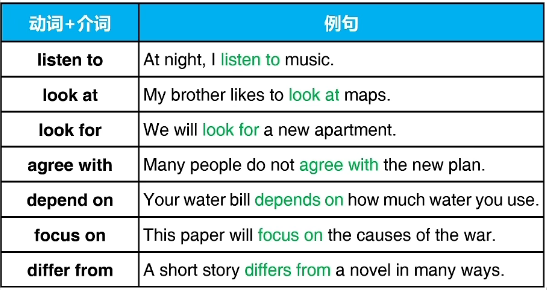

第九章 副词的基本知识
一、副词是什么
副词用于给句子增加更多信息
副词可以描述动词、形容词和其他副词
副词可以是一个词,也可以是一个介词短语
副词共六种:地点、时间、方式、频率、程度、确定性
每种不同的副词为句子增加不同的信息
地点:增加 Where 的信息 here,there,in this room
时间:增加 When 的信息 now,then,in the morning
方式:增加 How 的信息 quickly,well,carefully
频率:增加 How often 的信息 always,often,never
程度:增加 How much 的信息 very,so,extremely
确定性:描述内容的可能性 certainly,likely
二、地点副词和时间副词
1.作用
地点副词增加Where的信息
My new apartment is here, but my old apartment was near the lake.
时间副词增加When的信息
Joe and I watched a movie last night. It ended at 10 p.m.
2.常用地点副词和时间副词
地点 here,there,far,somewhere,in,on,at
时间 first,then,next, last, before, after, recently,soon,later,early, finally
3.温馨提示
地点副词和时间副词一般出现在句尾
Queen Elizabeth I was born in London.
She was born in 1926.
如果同时出现地点和时间,地点放在时间前面
Queen Elizabeth I was born in London in 1926.
如果地点或时间短语放在句首,需要逗号断开
如果只有一个词的地点或时间,一般不需要逗号断开
In France, people put sugar on their popcorn.
In 1926, Queen Elizabeth l was born in London.
Here you can see a map of China.
Yesterday we went to the bank and the post office.
First, you should read the text.
三、方式副词
1.作用
方式副词增加How的信息
You should fry the meat quickly to keep the flavor.
绝大多数方式副词是形容词加-ly
个别方式副词是例外情况
good-well
fast -fast
early -early
hard-hard
2.温馨提示
方式副词往往放在句尾
如果有宾语,方式副词建议放在宾语的后面
如果动词有两部分,方式副词可以放在中间
Our teacher spoke clearly.
He explained the new vocabulary carefully.
I can easily read this foreign language
四、频率副词
1.作用
频率副词增加How often 的信息
Kevin and I never eat lunch at noon. Our lunch is
always at 11:30 a.m.
2.常用频率副词
always,usually, often, sometimes, seldom, rarely,never
daily, weekly, monthly, yearly
3.温馨提示
频率副词一般放在be动词后,其它动词前
I am always late to meetings.
l always arrive late to meetings.
如果动词有两部分,频率副词一般放在中间
I can usually eat a whole pizza.
People should always lock their doors.
频率副词 sometimes 可以出现在句首、句中或句尾
Sometimes John and I watch TV at night.
John and I sometimes watch TV at night.
John and I watch TV at night sometimes.
五、程度副词
1.作用
程度副词增加How much的信息
The bus station was very crowded. It was extremely hot.
2.常用程度副词
completely, incredibly, exactly, extremely, really,hardly,barely,nearly,mainly,almost,only,just,quite,so,very, too.
3.温馨提示
程度副词too是负面含义
正确 The soup was too salty.
错误 The Soup was too delicious.
程度副词可以用在形容词或副词前
The test was extremely difficult.
She sings very well.
六、确定性副词
1.作用
确定性副词描述内容的可能性
Maybe he is right about this decision.
2.常用确定性副词
maybe, perhaps, likely, possibly, probably, clearly,obviously, certainly, definitely
3.温馨提示
确定性副词一般放在be动词后,其它动词前
The long-term effects of eating salty food are clearly harmful.
The Maya people likely disappeared due to a disaster.
maybe,perhaps,clearly,obviously 也可以放在句首
第十章 从简单句到复合句
一、什么是简单句
英语句子的基本要求:一组词,有完整含义,有主语,
有动词,大写字母开头,句号问号叹号结尾
简单句就是有一套主语+动词结构的句子
主语可以不止一个,动词也可以不止一个
但是主语+动词结构只能有一套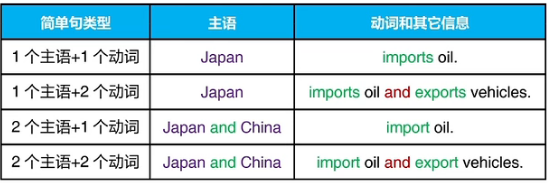
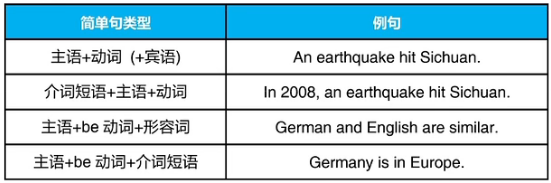
二、简单句的格式
1.陈述
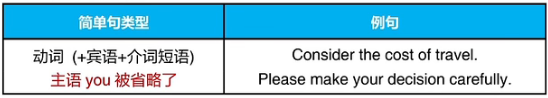
2.命令和请求(祈使句)
3.疑问
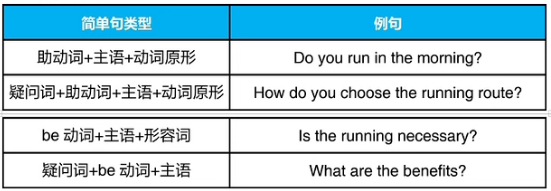
助动词:do,does,did,am,is,are,was,were,has,have,had,can,will
三、简单句的功能
1.陈述信息——简单句最常见的应用
2.发出命令、提出请求一用于指挥读者的行为
3.提出问题——引起读者关注,引发读者思考
四、什么是复合句
使用基本连词把两个简单句连在一起变成更长的句子,
称为复合句
复合句有两套或更多的主语+动词结构
基本连词 FANBOYS: for,and,nor,but,or,yet,so
复合句中两个简单句地位对等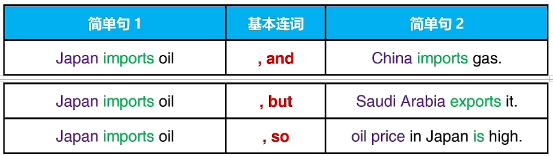
注意:
基本连词前面需要使用逗号断开
不要用基本连词连接两个独立句
五、基本连词的作用
for/and/nor/but/or/yet/so
and 补充额外信息 extra information
but 补充相反或对立的信息 opposite information
so 表示结果或目的 result/purpose
注意:常见错误
基本连词前面无逗号 Five is an odd number, but six is an even number.
基本连词使用错误 I like tea, but I drink coffee sometimes.
基本连词不连接两个独立句 Costa Rica is in Central America, and Peru is in South America.
两个句子不能逗号连接 July is usually a month with a great deal of rainfall, but this year it has been very dry.
六、基本连词的具体用法
1.and 的用法
两分句逗号断开、两词不需要逗号、三者列举要逗号
China is in Asia**, and** it has a large population.
China is in Asia and has a large population.
China and Japan are in Asia
China,Korea, and Japan are in Asia.
2.but 的用法
两分句逗号断开、两词不需要逗号
Shanghai is a large city, but it is not China’s capital.
The weather in January is sunny but cold.
I feel nervous but excited.
3、so 的用法
表示结果,所以:需要逗号断开
表示目的,为了/这样才能:不需要逗号断开
I study hard, so I have a good grade in the exam.
I study hard so / so that I can have a bright future.
第十一章 复杂句的基本认知
一、什么是复杂句
复杂句是另一种更长的句子
复杂句由主句和从句构成
主句和从句都有自己的主语+动词结构
主句可以自己独立存在,从句不能自己独立存在
二、常用的复杂句连接词
because, after, before, when, as soon as, if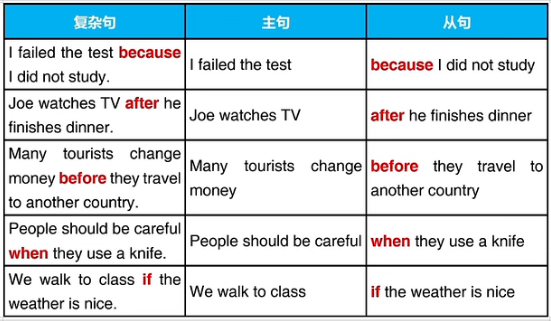
三、复杂句的语序
一般情况下,主句在前,从句在后,连接词在从句开头,
不需要逗号断开
John is hungry now because he did not eat lunch.
从句也可以放在前面,需要逗号与主句断开
Because John did not eat lunch, he is hungry now.
如果句子里有名词和代词,则名词先出现,代词后出
现,不管前面的是主句还是从句
John is hungry now because he did not eat lunch.
Because John did not eat lunch, he is hungry now.
四、使用because表示原因
以because开始的从句叫原因从句
原因从句里的动词可以是过去、现在或将来
原因从句放在句首,要用逗号和主句断开
Because the car was expensive, Pablo did not buy it.
Pablo did not buy the car because it was expensive.
五、使用 after、before、when 和 as soon as 表示时间
after、before、when 和 as soon as 表示从句和主句的时间关系
以 after、before、when 和 as soon as 开始的从句叫时间从句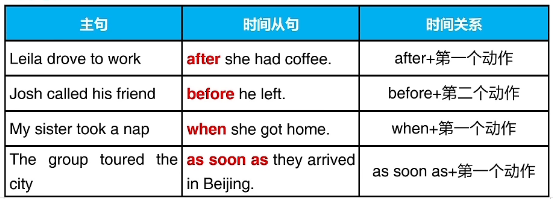
时间从句放在句首,要用逗号和主句断开
Before Omar went to the airport, he packed his suitcase.
Omar packed his suitcase before he went to the airport.
六、使用if表示条件
if开始的从句用于给出主句的条件
以if开始的从句叫条件从句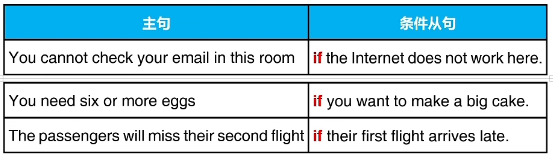 条件从句放在句首,要用逗号和主句断开
条件从句放在句首,要用逗号和主句断开
If we have extra time, we want to play basketball.
We want to play basketball if we have extra time.
重要考点:主将从现
与将来有关的时间从句和条件从句,主句使用will或be going to,从句使用一般现在时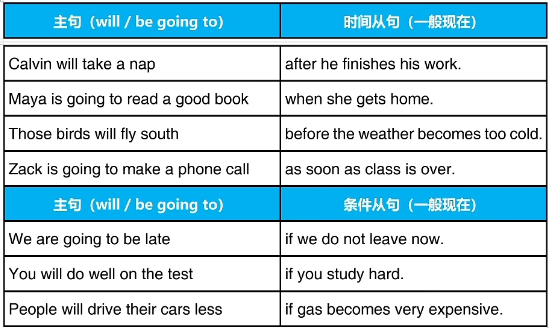
第十二章 名词性从句的作用
一、名词性从句
名词:人物、事物、地点,可以做主语或宾语
英语句子:一组词,有完整含义,有主语,有动词
从句:由引导词开始的句子,不能脱离主句独立存在
疑问词:提出问题的词,如who/whom,what,whose,
which,when,where,why,how,how many,how much,how often 等
名词性从句就是一个从句作为名词,由that、疑问词或if/whether 引导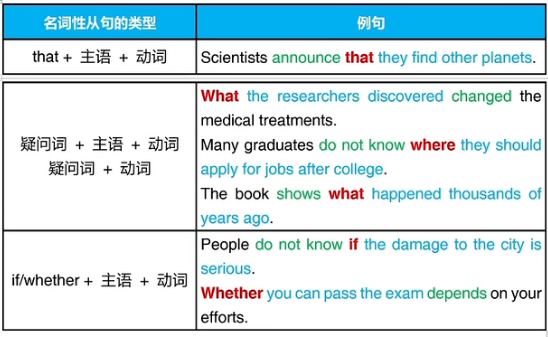
注意:
1、名词性从句视作单数名词,动词需要使用单数
How often people change careers is (be) an interesting question.
2、that 从句作宾语时,that 可以省略
Research suggests (that) salty food is harmful to your health.
3、注意名词性从句中主语和动词的顺序
错误 They are not sure who is he.
正确 They are not sure who he is.
名词性从句常见错误
1、从句中主语和动词的顺序
2、从句视作单数名词,作主语的从句与动词保持一致
二、名词性从句的作用
1.提出想法和观点
Jean Piaget, a Swiss psychologist, believe that the thinking process in children is different from that in adults.
2.描述发现和具体情况
Scientist find that English learning in childhood is beneficial.
Recent studies show that generous people are generally happier than others.
3.给出建议或推荐(应用)
Health experts recommend that adults should get between seven and eight hours of sleep each night.
三、名词性从句的位置
1.作为动词的主语
Which career a person chooses tells a lot about his
or her personality.
Whether a business will succeed or fail depends on
several factors.
2.作为动词的宾语
Until 1897, doctors did not know how they could cure some disease.
A recent survey of college students shows that many do not plan to attend graduate school.
常见相关动词:announce, ask, believe, claim, conclude, indicate, know, note, report, say, show, state, suggest, think 等
3.作为介词的宾语(在这种情况下不使用that)
The workers receive training in how they can handle different situations.
He received a letter about what he should prepare for the college.
4.在“be 动词+形容词”之后
It is clear that many students do not completely understand English grammar.
It is true that repeat customers are important to a business.
常见相关形容词: aware, certain, clear, obvious, sure, worried 等
5.在某些名词后,给出具体内容
He raises an idea that today’s parents try to manage their children’s lives.
The fact that global warming becomes serious continues to be a hot topic.
He left a message that he would come later.
常见相关名词:idea,news,fact,sign,promise,question, thought, hope, message, suggestion,decision,evidence 等
名词性从句中that与what的区分
that 用于陈述句,句子内容完整
what 用于提出问题,句子内容不完整
第十三章 定语从句的基本作用
一、什么是定语从句
形容词:给出人物、事物或地点相关信息的词
英语句子:一组词,有完整含义,有主语,有动词
从句:由引导词开始的句子,不能脱离主句独立存在
定语从句就是一个从句作为形容词,由who,which,that,whom引导
定语从句在它要描述的名词、名词短语或代词之后,引导词对应定语从句要描述的名词、名词短语或代词
定语从句就是形容词从句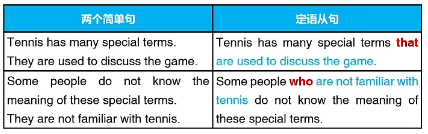
二、定语从句的构成
1.找到两句话的共同名词
2.保留主句的名词,去掉从句的名词
3.使用引导词把从句安在主句名词的后面
4.引导词基本原则:人使用 that/who/whom,物使用 that/which
三、定语从句的引导词
1.引导词在从句里作主语

2.引导词在从句里作宾语(可以省略)
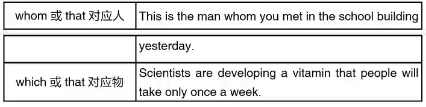
3.引导词在从句里作介词的宾语
第十四章 状语从句的基本作用
一、什么是状语从句
副词:给句子增加更多信息
英语句子:一组词,有完整含义,有主语,有动词
从句:由引导词开始的句子,不能脱离主句独立存在
状语从句就是一个从句作为副词,为句子增加更多信息
状语从句的引导词表示从句和主句的关系
状语从句可以放在主句前,也可以放在主句后,放在主句前需要逗号断开
状语从句就是副词从句
二、常见的状语从句引导词

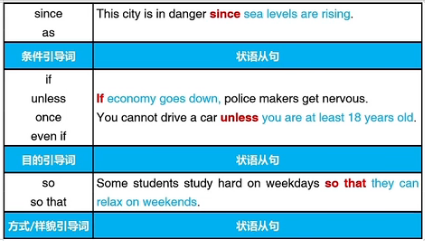

注意:
1、状语从句在主句之前,需要逗号断开
2、状语从句不能自己独立成句
3、状语从句和主句必须都是完整句
4、主从句只需要一个引导词
第十五章 动词的现在进行时
一、什么是现在进行时
现在进行时表示现在正在发生的动作
狭义现在:准确的现在这一刻(即时)
模糊的现在这一段(暂时)
二、现在进行时的构成
be动词+动词-ing 形式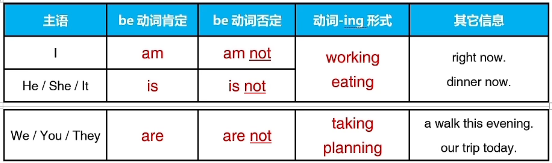
三、动词-ing形式的变化:动词+ing
1.动词末尾直接加-ing
We are working on our final projects this week.
No one is eating in the cafeteria right now.
2.以字母 e 结尾的动词,去 e 加-ing;以字母 ee 结尾的动词,直接加-ing
Many people are taking the train because of the snow.
I am baking a cake for my friend’s birthday.
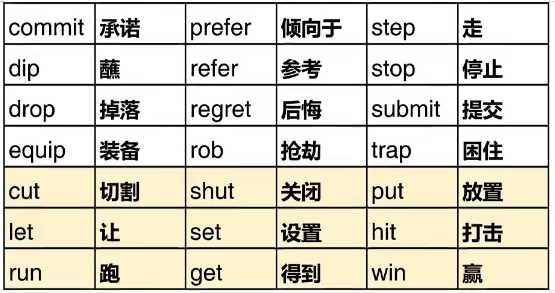
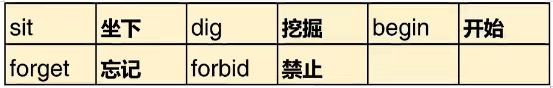
3、以重读闭音节辅音元音辅音结尾的动词,双写最后一个字母,再加-ing
We are planning our class project.
The janitor is mopping the floor.
需要双写加-ing的常见动词:45个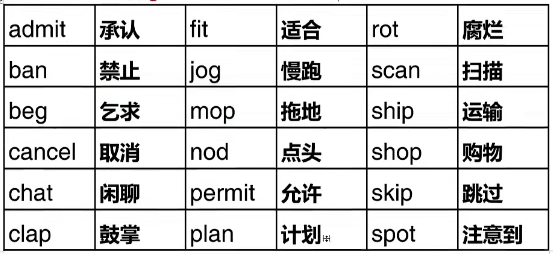
4.以-ie结尾的动词,-ie变-y再加-ing
The children are tying their shoes.
Those plants are dying.
四、现在进行时句子里时间副词的位置
1.today, now, nowadays, at this time, these days, this week,this year 等,可以放在句首或句尾。多数时间短语放在句首需要逗号断开
Wildlife biologists are tracking bears this year.
This year, wildlife biologists are tracking bears.
2.类似 currently 或 presently 等副词,可以放在句首、 句中和句尾。在句中时,放在两个动词中间
Presently, the support rate of the government is growing.
The highway department is currently building fences to protect deer.
3.still 放在两个动词中间
For economic reasons, many people are still living without health care.
五、现在进行时的作用
1.描述某个动作正在发生,可以是现在的这一刻,也可以是现在这一段时间
The president is visiting two foreign countries this week.
I am looking forward to see you in the university campus.
2.表示现在的情况正在发生变化
Since the cost of parking is increasing, more and more people are sharing rides to work and school.
3、强调动作反复发生,经常和always或still连用,有抱怨或责备的语气
You are always making promises.
Most places have Internet security, but viruses are still getting into computer systems.
注意:一般现在时用于表示习惯、常规和日常情况(发生许多次的动作、一直都这样的动作)
第十六章 动词的过去进行时
一、什么是过去进行时
过去进行时表示过去正在发生的动作
过去:准确的过去某一刻时间
模糊的过去某一段时间
二、过去进行时的构成
be动词+动词-ing形式(was/were+doing)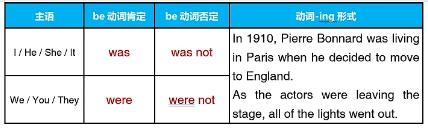
三、过去进行时的用法
1.描述在过去某个特定时间正在发生的动作
The economy was showing signs of failing in 2015.
At 10:30, the crowd was gathering outside the town hall.
2.描述某个过去被突然中断的动作(重要考点)
使用while/as+过去进行时描述被突然中断的动作
使用when+一般过去时描述中断原因
My friends were driving through town when the earthquake hit.
As they were approaching the top of Mt Everest,Bishop and Jerstad noticed that their oxygen was low.
One of the front tires blew out while the pilot was landing the plane.
3.描述故事背景或生动形象的场景
It was an ordinary day at work. Dave was working at his desk. His colleagues were doing research on that strange equipment
注意:一般过去时用于陈述过去结束的事件
第十七章 动词的现在完成时
一、什么是现在完成时
现在完成时是正常时态表达的最后一个诉求
现在完成时是基本时态含义的最后一块拼图
现在完成时是唯一打破过去现在界限的时态
These people have lived in this area for almost a century.
Many citizens are upset because the government has increased taxes.
They have won three times this year.
二、现在完成时的构成
助动词have/has+过去分词(have/has+done)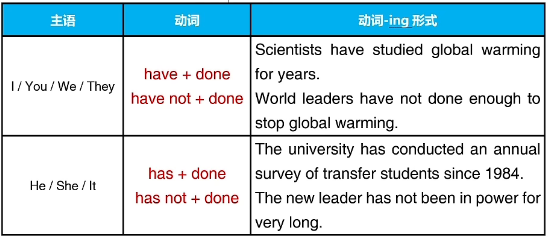
记忆三原则:简单、熟悉、重复
三、分词的基本概念
分词有现在分词和过去分词两种
现在分词:动词-ing形式(参看现在进行时部分)
过去分词:动词-ed形式(参看一般过去时部分)
四、每个动词需要掌握的形式变化
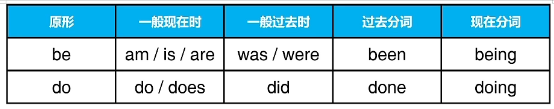
五、现在完成时的作用
1.动作开始于过去,持续到现在
Brasilia has been the capital of Brazil since 1960.
Government officials have known about this problem for decades.
Researchers have not discovered a cure for cancer yet.
常见时间词
1、Since+过去时间点:自从过去到现在
2、for+时间段:一段时间(几乎可以用于任何时态)
3、其它时间短语
by now到目前为止
up to now 到目前为止
over/in the past 3 years 在过去的一段时间里
recent/recently 最近
2.描述从过去到现在动作发生的次数
Humans have landed on the moon about 15 times.
This area has never experienced an earthquake.
Have you ever experienced a natural disaster?
This is the first time I have finished a task by myself.
3.用现在的语境匹配过去已完成的动作
站在现在说过去,需要把过去和现在连接起来
I parked my car in front of your house. It has disappeared now.
My son came home for the summer vacation. Now he has gone back to the university.
The government has passed a new tax law that will have an immediate impact on citizens.
Many people have criticized this new requirement because it is not fair.
Only twelve people have walked on the moon. One of the most famous one is Armstrong.
重要考点:区分一般现在时和现在完成时
一般现在时:表示习惯、常规和日常情况(发生许多次的动作、一直都这样的动作)
现在完成时:表示动作在过去和现在的时间关系
第十八章 动词的过去完成时
一、什么是过去完成时
过去完成时用于强调在过去动作或过去时间点之前已经结束的动作
By nine o’clock last night, we had got 200 pictures from the spaceship.
I thought I had sent the letter a week before.
When I woke up, the rain had already stopped.
二、过去完成时的构成
助动词 had+过去分词(had + done)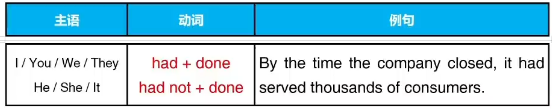
三、过去完成时的用法
1.明确两个过去结束的动作里最早的动作
注意:需要两个过去动作、需要分出先后顺序
By the end of last term, we had learned 5000 new words.
By the time of last year, we had built two bridges.
The bus had already left by the time I got there.
常见时间词
by+过去时间/by the time+过去时间:到过去时间为止(短语/从句)
注意:如果动作时间明确,或出现before 或 after 等描述动作先后的时间状语从句,不需要使用过去完成,使用一般过去即可
2.描述过去的虚假的条件(不是考点,只要看懂)
If I had known your telephone number,I would have called you.
重要考点:过去时态的正确应用
一般过去:陈述过去结束的事件
过去进行:描述过去某个特定时间正在发生的动作
描述某个过去被突然中断的动作
描述故事背景或生动形象的场景
过去完成:明确两个过去结束的动作里最早的动作
四、时态总结:七种时态的作用
1.只与现在有关的两种时态
一般现在:表示习惯、常规和日常情况
发生许多次的动作,一直都这样的动作
现在进行:描述某个动作这一刻或这一段正在发生
表示现在的情况正在发生变化
强调动作反复发生,有抱怨或责备的语气
2.只与过去有关的三种时态
一般过去:陈述过去结束的事件
过去进行:描述过去某个特定时间正在发生的动作
描述某个过去被突然中断的动作
描述故事背景或生动形象的场景
过去完成:明确两个过去结束的动作里最早的动作
3.与过去和现在有关的一种时态
现在完成:表示动作在过去和现在的时间关系
4.与将来有关的一种时态
一般将来:描述将来的预测和预期、计划和提议
第十九章 谓语和非谓语
一、什么是谓语?
谓语描述句子主语的动作或状态特征
谓语指明主语“做什么”、“是什么”或“是什么样的”
谓语可以是单独动词的时态变化,可以是动词加形容词,还可以是情态动词加动词
谓语有主动和被动两种不同的形态
I made your birthday cake last night.
Your birthday cake was made by me last night.
This book is my gift for you.
I felt tired after a day’s work.
My pen is in my bag.
I can finish the task on my own.
This city was built in Tang Dynasty to defend people
二、情态动词
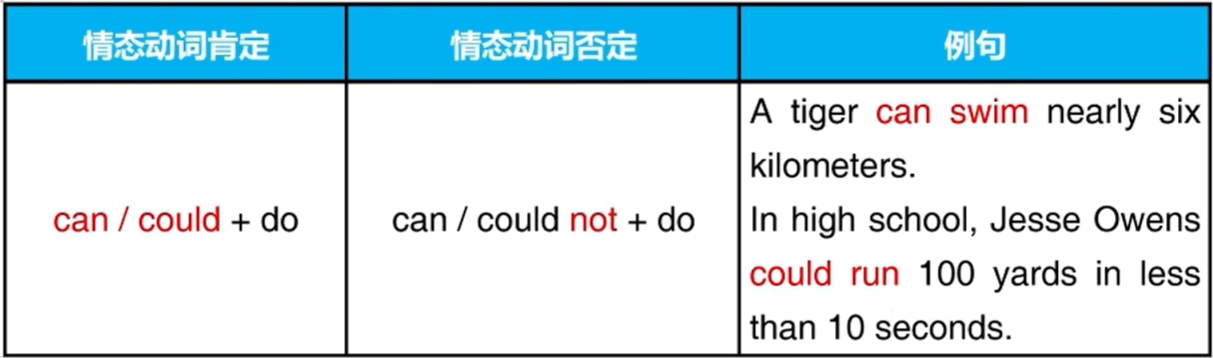
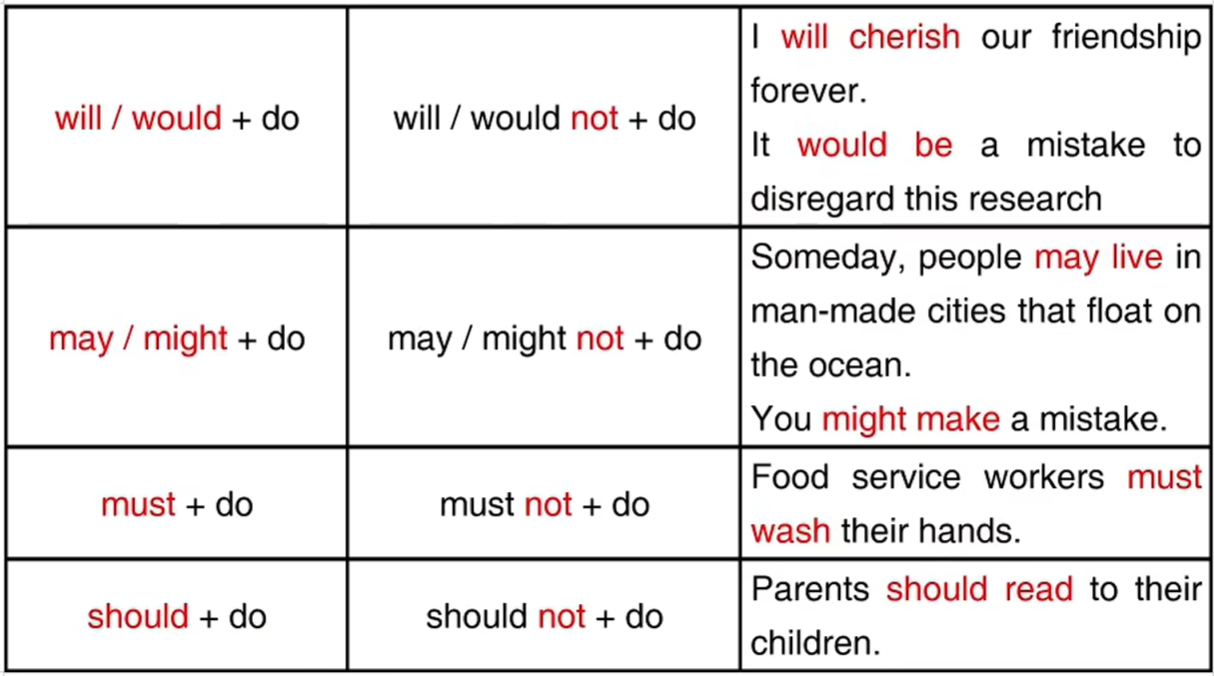
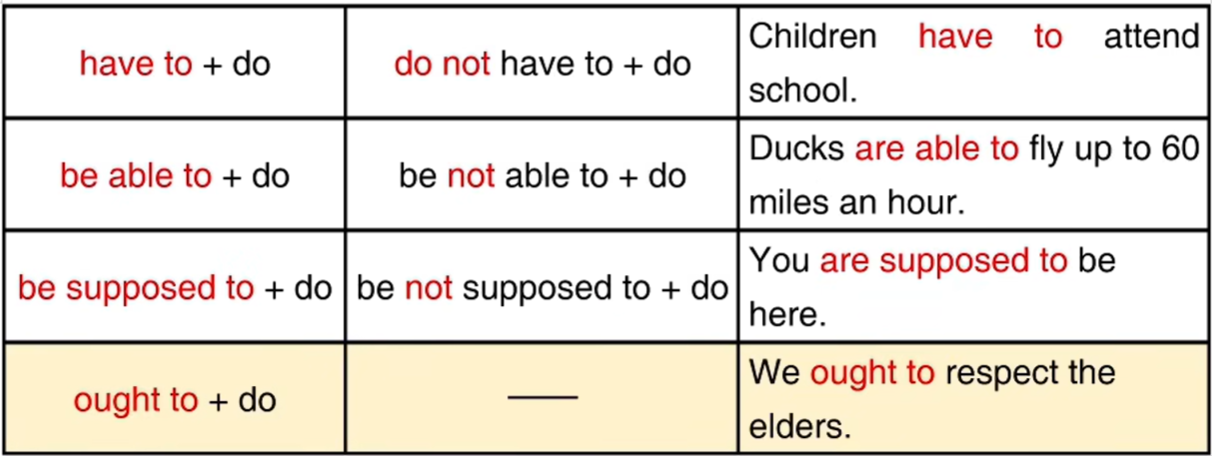
三、情态动词的作用




四、被动语态
在被动语态的语句中,动作的宾语处于主语的位置
主动: The doctor examined the child.
被动: The child was examined (by the doctor)
五、被动语态的变化
动词变为 be 动词+过去分词 ( do 变为 be+done )
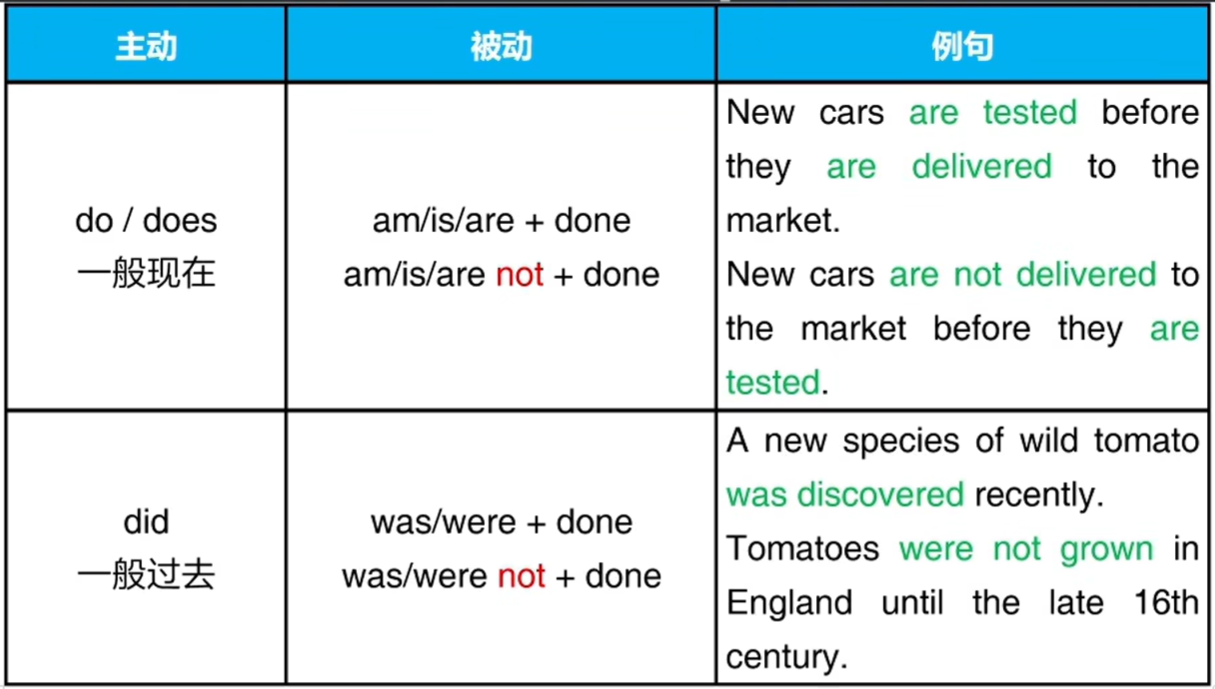
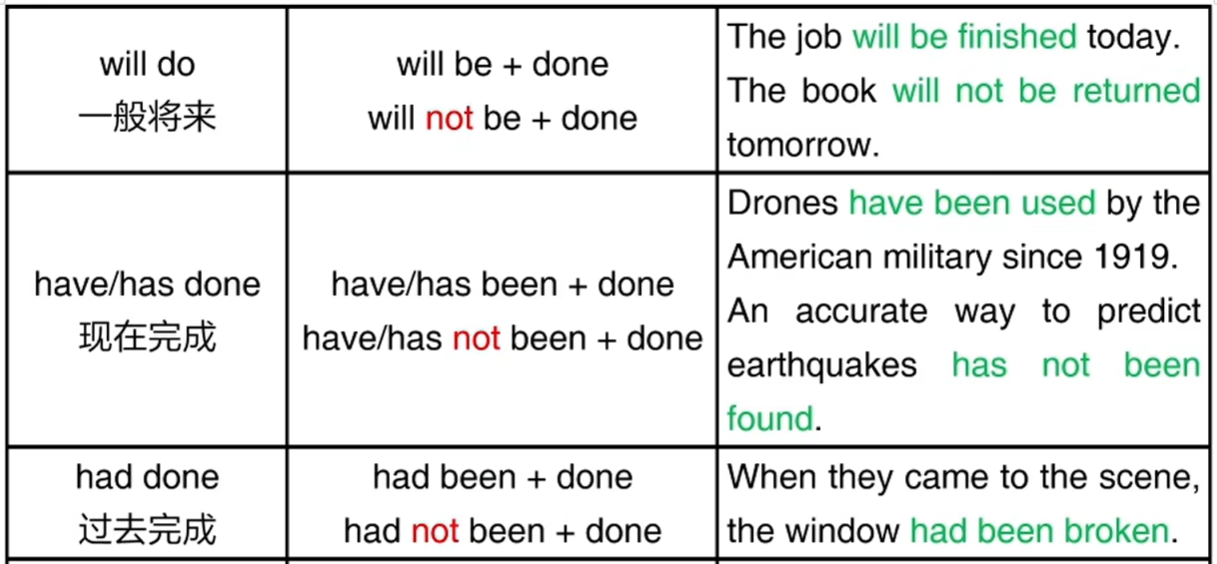


注意:
1、动作有宾语,才能变成被动语态
2、注意 be 动词或助动词要和主语保持一致
3、如果不需要强调动作发出者, “by短语” 可以省略
4、进行时的被动比较罕见,可以忽略
5、动词过去分词的变化必须掌握
重要考点:非谓语动词的基本形态
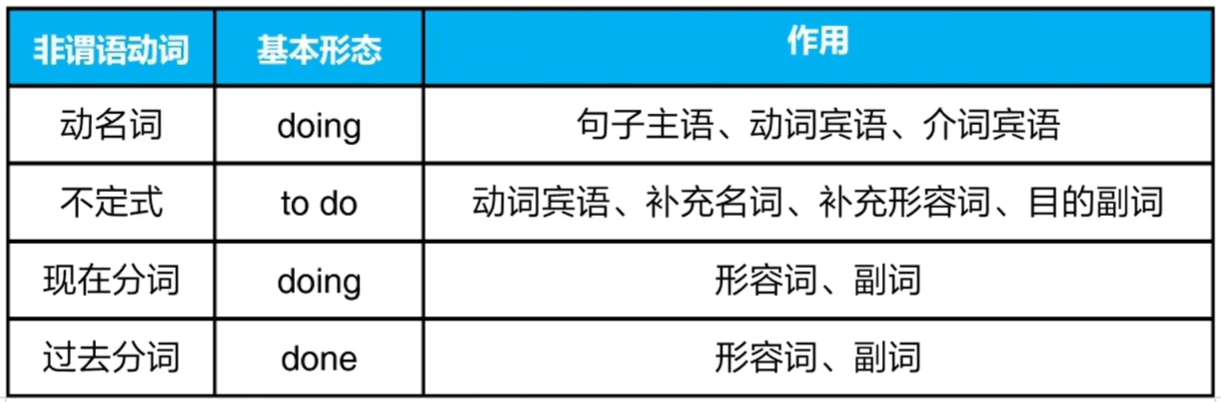
注意:
1、非谓语动词的否定直接在前面加 not
2、动名词是单数名词
3、不定式 to do 一般不用作主语,也不作介词宾语
第二十章 句子结构的拆分训练
一、句子里有什么
英语句子的基本要求:一组词,有完整含义,有主语
有动词,大写字母开头,句号问号叹号结尾
主语、动词、宾语
形容词、副词、介词短语
基本连词、主从句、非谓语动词
重要考点:非谓语动词的基本形态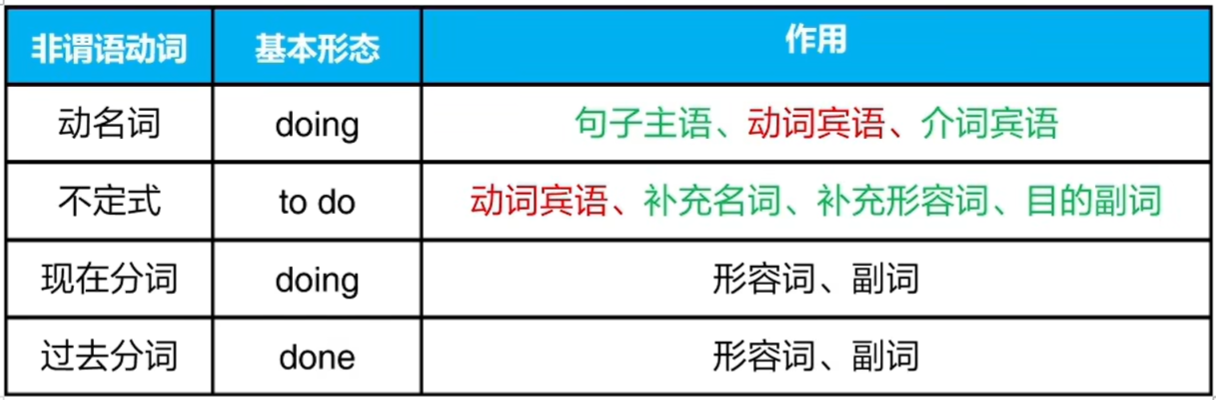
重要考点:动词后面的宾语是不定式还是动名词
如果动作是目的,则使用to do
如果动作不是目的,则使用doing
重要考点:介词后面要使用动名词
重要考点:使用动名词而不是普通动词作主语
重要考点:使用动名词作主语,动词要使用单数
二、现在分词和过去分词作形容词的用法
常规用法

描述情绪感受

三、形容词从句与分词的转换规则
1、出现be动词的形容词从句,省略引导词和be动词
2、常规动词的定语从句,省略引导词,动词变成doing
注意:从句转换为分词,务必省略到位
四、副词从包与分词的转换规则
1、前提条件:主句与副词从句主语相同
可转换 When I saw his face,I recalled his name.
不可转换 When he greeted me,I replied warmly.
2、出现be动词的副词从句,省略从句主语和be动词描述同时的时间副词从句,引导词可以一并省略
When people are stressed, they exhibit high blood pressure and accelerated heart rates.
When stressed, people exhibit high blood pressure and accelerated heart rates.
Stressed, people exhibit high blood pressure and accelerated heart rates.
3、常规动词的副词从句,省略主语,动词变成doing 描述同时的时间副词从句,引导词可以一并省略
When people sleep with pressure, they dream four to six times each night
When sleeping with pressure, people dream four to six times each night.
Sleeping with pressure, people dream four to six times each night
4、描述原因的副词从句,省略引导词 because或since,动词变成 doing
Because the students had read the instruction, they were able to carry out the experiment alone.
Having read the instruction, the students were able to carry out the experiment alone.

完结撒花
